

RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) has been described as one of the ten most critical technologies of this century. RFID has been used in more areas, such as identifying and sorting goods in logistics companies, access control, personnel management in general enterprises, merchandising, and record-keeping in major supermarkets. However, the rapid identification of items is already a must-have technology for all industries, so how can we quickly identify goods? RFID technology is one of the answers.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses radio waves to transmit data from RFID tags' chip that can record a unique number or information, can be used in a wider range of applications than barcodes. For example, the chip in the identification card records attendance records, the location, time, and other information.
RFID system uses wireless operation, so the connection between Tags and Reader does not need to face each other to be detected. RFID sensing distance is longer than bar codes and easily penetrates the fabric, plastic, paper and other obstacles. The following is a schematic diagram of the RFID system operation.
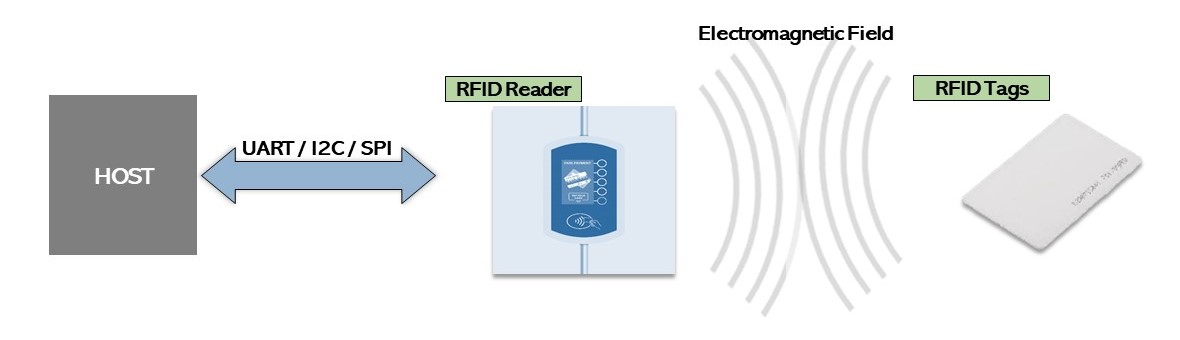
Radio waves are transmitted digital signals on the RFID reader, which need to be modulated into a carrier wave. After activation, the reader will continuously emit electromagnetic waves, when received by the Tags’ antenna, will convert them into electrical energy and send back the tags data via radio waves.
RFID uses the internal microchip to access data, which chip-size is only grain size, and can store more data.
RFID has different frequency specifications and communication frequencies as well as communication protocols. The following table lists the common RFID frequencies and their uses.
| Low Frequency (LF, 30KHz ~ 300KHz) |
High Frequency (HF, 3MHz ~ 30MHz) |
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF, 300MHz ~ 1GHz) |
Microwave (1GHz and above) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 125KHz | 13.56MHz | 860MHz ~ 960MHz | 2.45GHz |
| Max. reading range (Passive) |
< 0.5m | < 1m | 3m | > 4m |
| Tab Type | Passive | Passive | Passive / Active | Passive / Active |
| Note | Data Transfer-speed slow | Used for short distance reading of multiple tags | Fast access speed | Highest access speed and longest transfer distance |
| Applications | Anti-theft system, access control, store sales management | Library asset management | Production Line, Inventory Management, Electronic Payment System | Logistics, baggage management |
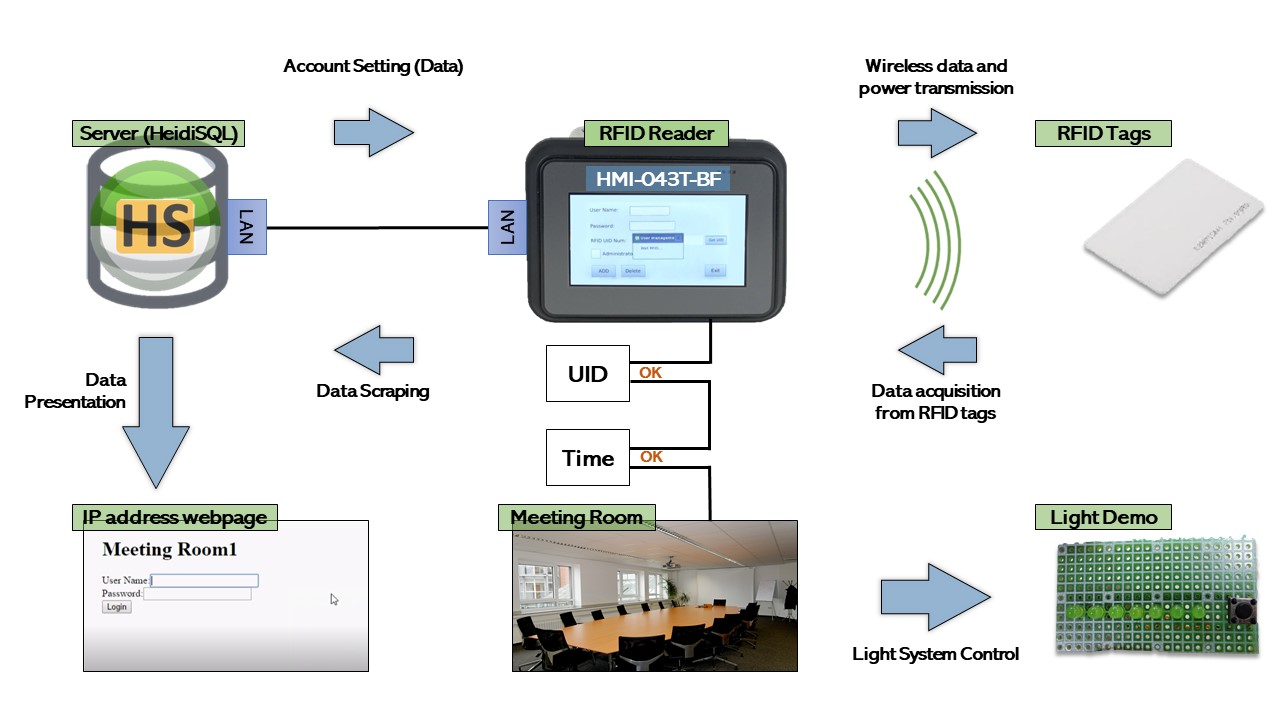
The HMI-043T-BF is used as RFID reader. When this device scans the RFID tags, if the UID inside the tag is not used yet, it can be registered through the user interface and the UID, name and password will be recorded in the database using the server (HeidiSQL); if the UID is already registered, the meeting room can be booked, and cannot be selected on the time slot which other users chose.
| Project Name | HMI-043T RFID Meeting Room Booking System Demo Project |
| Functions | 1. Connects to the Server via LAN 2. RFID Functions Support 3. Light Control System |
| Prepare | 1. RFID Tags x2 (A Company / B Company) 2. HMI-043T (Built-in RFID Reader + Linux) 3. Simple Lighting Device 4. Server (HeidiSQL_9.4.0) |
| Work Procedure | 1. Set an administrator RFID account on the server 2. Set RFID accounts for members on the server 3. Login as the user using the browser via cellphone or computer. The server address should be http://[IP Address] on HMI-043T/Login Ex: http://192.168.3.15/Login 4. Logging into the account and select the time you want to use the meeting room. 5. The system will be unable to be accessed if the user has not scheduled a meeting during specific time. 6. Logging into the meeting room system by RFID card, and the user can control the lights. |
*If you are interested in this demo, please contact info@icop.com.tw for more detail information.
Features of HMI-043T-EM4XX-BF02:
Please write to info@icop.com.tw, call your nearest ICOP Branch, or contact our Worldwide Official Distributor for more info and sample request.